rewrite this content using a minimum of 1200 words and keep HTML tags
In recent years, investor attention has been fixated on the “Magnificent Seven,” especially Nvidia, whose shares have skyrocketed by hundreds of percent. The explosive rise of artificial intelligence (AI) across industries has radically transformed the investment landscape and propelled corporate profits to new heights. This has attracted investments worth hundreds of billions of dollars.
Source: publiccomps
But the AI revolution isn’t just about cloud players and chipmakers. Data centers — or as Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang calls them, “AI factories” — are massive facilities that require far more than just top-tier chips. Let’s take a look at the companies quietly benefiting in the background from the growing AI investment boom.
Phase One of AI: Compute Power
Before your ChatGPT prompt turns into a meaningful response, several key processes occur:
Your data is sent to the cloud, where it’s processed by high-performance chips in data centers. This stage involves companies like Nvidia, AMD or Broadcom, which specialize in developing advanced GPUs, CPUs, and accelerators — essential components for the massive computations AI models demand.
While major cloud players are the largest customers of these firms, many are now developing their own chips to save costs. Amazon has its Trainium and Inferentia chips, Google has Tensor, and Microsoft has Maia. These could become serious competitors to established chip giants. At the same time, they present an opportunity for TSMC, the dominant player in chip manufacturing.
Phase Two of AI: Infrastructure
To function, these chips require vast technological infrastructure. They need to communicate with one another, store data, and operate continuously — all while consuming enormous amounts of electricity and generating heat. This creates opportunities across several sectors:
Networking equipment – Crucial for transferring huge volumes of data and enabling server communication. Besides Nvidia’s own solutions, competitors here include Broadcom, Cisco, and Arista.
Data storage and memory – AI models must store vast amounts of data. High-speed memory chips like HBM3 or advanced SSDs face relentless demand. Key players include Micron and Samsung.
Servers, cooling, and backup power – These ensure uninterrupted operation of data centers. AI models require cutting-edge cooling systems and specialized servers. Leading companies here include SuperMicro and Dell.
Renewable energy – Data centers have extreme energy needs and rely on consistent power supply. This benefits energy providers, particularly in regions like Texas or Virginia. Companies like Vistra and NRG Energy are already seeing a clear uptick in demand.
Phase Three of AI: Applications
Once companies secure the infrastructure from phases one and two, the key question becomes: How can AI drive revenue and profit growth? This phase currently includes software companies that can use AI to boost the efficiency of their products. Examples include:
Social media and advertising – AI improves ad targeting and content personalization
Cybersecurity – AI helps detect and block cyber threats
E-commerce – AI personalizes offers, enhances customer support, and optimizes logistics
Healthcare – AI assists in diagnostics, drug research, and improving patient care
Media – AI generates content, analyzes trends, and automates production
Mobility – AI powers autonomous driving, seen as the future by many auto companies
Companies in this third phase are often more resilient to geopolitical risks, such as trade wars. This is where some of the biggest investment opportunities could emerge in the coming years.
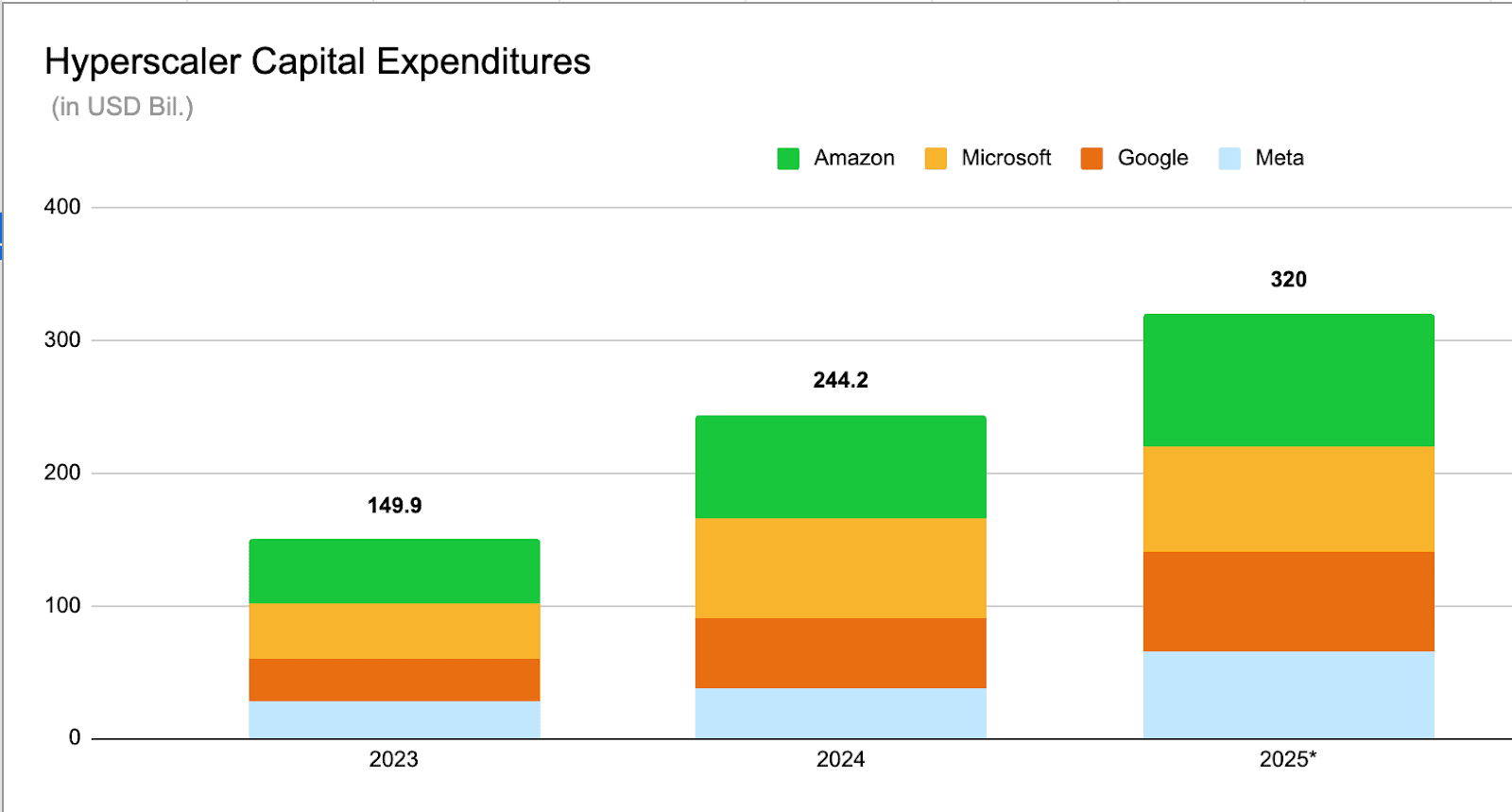
Source: eToro
As we can see, AI investments continue to surge. The four largest cloud giants in the U.S. alone plan to invest more than $300 billion next year, with a significant portion directed toward AI infrastructure. On top of that, governments are supporting AI development — in the U.S., for instance, through the Stargate project, which is already channeling the first tranche of a planned $500 billion investment over the next four years.
Much of this capital may benefit smaller, specialized companies that focus on key components of the AI ecosystem — from networking and energy to servers, software, and applications. The AI revolution is still in its early days, and more investment opportunities are likely to emerge in the years ahead.
While Nvidia and other tech giants dominate the headlines, the real investment gems often lie in the shadows — among the enablers of infrastructure, energy, and supporting technologies. Keep an eye not just on the chips, but also on the companies powering this technological revolution behind the scenes.
This communication is for information and education purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, a personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to buy or sell, any financial instruments. This material has been prepared without taking into account any particular recipient’s investment objectives or financial situation and has not been prepared in accordance with the legal and regulatory requirements to promote independent research. Any references to past or future performance of a financial instrument, index or a packaged investment product are not, and should not be taken as, a reliable indicator of future results. eToro makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this publication.
and include conclusion section that’s entertaining to read. do not include the title. Add a hyperlink to this website http://defi-daily.com and label it “DeFi Daily News” for more trending news articles like this
Source link



















